PPE Provider in Africa - Safety Shoes for Africa - Personal Protective Equipment for Africa - Mining Workwear for Africa - Petrol Workwear for Africa - Safety Boots for Africa
OUR PPE PRODUCTS
Here, you will find all our safety equipment & PPE (Personal Protective Equipment) !
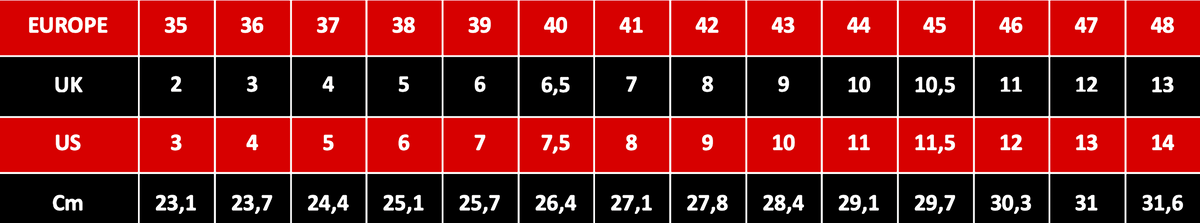
AllSafety ShoesRangersGumbootsHead ProtectionEye ProtectionMining GarmentsPetrol WorkwearCotton WorkwearRain Protective ClothesHigh Visibility ClothesDisposable MasksDisposable CoverallsLoad MoreSIZE CORRESPONDENCE TABLE :

SAFETY STANDARDS
What are the standards for
Safety shoes ?ISO STANDARDS
EN ISO 20344 : Test methods for safety shoes
Standards summarizing all the tests and test methods performed on safety shoes before they are placed on the market. This Standard is used in conjunction with EN ISO 20345 and EN ISO 20347 which define the basic and additional requirements for safety footwear
EN ISO 20345 : Specification of safety shoes for professional use
This international standard specifies the basic and additional (optional) requirements for general purpose safety footwear. The safety shoe is equipped with a safety toe resistant to impacts equivalent to 200 joules and crushing of 15 KNEN ISO 20347 : Specifications for work footwear for professional use
This footwear is different from safety footwear by the fact that these do not have toe caps against injury from falling objects or crushing impacts
SLIP RESISTANCE
SYMBOLS & TYPES OF FLOORS
SRA Hard industrial indoor floors (tile type)
SRB Hard industrial indoor or outdoor floors
(paint or resin type)
SRC SRA + SRB = SRC indoor or outdoor floors
(polyvalent type)GENERAL REQUIREMENTS


ADDITIONAL SPECIFICATIONS
In addition, there are particular markings for particular specifications :
AN : Protection of the malleolus
C : Conductive because electrical resistance does not exceed 100kW
CI : Cold insulation
CR : Upper cut resistant
ESD : Dissipative shoe
HI : Heat insulation
HRO : Heat resistant outsole up to 300°C (for 60 seconds)
M : Metatarsus protection against choc impacts
WR : Water resistant (waterproof)RECOMMENDED STORAGE CONDITIONS
We recommend storing safety shoes as follows :
- Do not compress or bend
- Do not store near steam pipes, radiators or other sources of artificial heat or expose directly sunlight, artificial light or other sources of ozone
- Storage ambient temperature must be between 10° C and 21° C. Storage temperature should not exceed 35° C
What are the standards for
Workwear ?GENERAL PERFORMANCE OF WORKWEAR
ISO 13688:2013
The ISO 13688:2013 standard, together with its amendment A1:2021, defines the general requirements applicable to protective clothing. More specifically, it addresses aspects such as ergonomics, safety (innocuousness), sizing, ageing, marking, and the information to be provided by the manufacturer. This standard does not, by itself, define performance levels for protection but must be used in conjunction with other standards that specify those protective requirements.
In detail, the ISO 13688:2013+A1:2021 standard specifies :
General requirements : Ergonomics, safety (innocuousness), durability, ageing, sizing, and marking of protective clothing
Innocuousness : The materials and components used must not cause harm, allergies, irritation, or injury to the user
Sizing : Sizes must be defined according to the user’s body measurements
Marking and information : Garments must feature appropriate marking and be accompanied by clear and precise information provided by the manufacturer
Non-standalone standard : This standard must be used in conjunction with other specific standards that define the required protective performance (against heat and flames, chemical or mechanical risks, etc.).
THERMAL PROTECTIVE CLOTHING
EN ISO 11612:2015
The EN ISO 11612:2015 standard specifies performance requirements for protective clothing designed to protect against heat and flames, including indices A1, A2, B1, C1, and F1. These indices indicate the level of protection the garment provides against different types of heat and flame exposure
The indices A1, A2, B1, C1, and F1 mean :
- A1 and A2 : Indicate limited flame spread. A1 refers to surface ignition, while A2 refers to edge ignition
- B1 : Indicates resistance to convective heat (heat transmitted by air movement)
- C1 : Indicates resistance to radiant heat (heat transmitted by radiation)
- F1 : Indicates resistance to contact heat
In summary, a garment certified to EN ISO 11612:2015 with indices A1, A2, B1, C1, and F1 provides limited protection against flame spread, as well as protection against convective, radiant, and contact heat

NFPA 2112
NFPA 2112 is the American standard from the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) that specifies the minimum requirements and test methods for protective clothing against flash fire hazards in industrial environments. It establishes performance criteria for fabrics and garments to protect workers from thermal burns in the event of a sudden fire
Key points of the NFPA 2112 standard :
Protection against flash fires : The standard is designed to protect against flash fires, which are sudden and brief bursts of flames
Minimum requirements : NFPA 2112 defines minimum requirements for flame resistance, durability, and protective clothing design
Test methods : The standard includes specific test methods to evaluate the performance of materials and garments, such as the flame resistance test
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) : Garments compliant with NFPA 2112 are considered Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and are commonly used by workers in the oil, gas, chemical industries, and other high-risk environments
ELECTROSTATIC PROTECTIVE CLOTHING

EN 1149-5:2018
The standard EN 1149-5:2018, in French, concerns protective clothing with electrostatic properties. It specifies the requirements related to the materials and design of these garments, which are intended to dissipate electrostatic charges and prevent the risks of ignition or explosion in environments where explosive atmospheres may be present
Protection against electrostatic discharges : The standard aims to prevent potentially dangerous sparks caused by static electricity, which can ignite flammable gases or dust in hazardous areas
ATEX zones : Garments compliant with the EN 1149-5 standard are particularly important in ATEX zones (Explosive Atmospheres), where the risk of explosion is higher than average
Grounding system : The standard specifies that garments must be used in conjunction with a grounding system (e.g., conductive footwear) to ensure proper dissipation of charges
Design and materials : The standard details the requirements related to garment design (closures, areas to cover, etc.) as well as the materials used, including conductive fibers (carbon, etc.) that enable the dissipation of static electricity
Performance requirements : The standard specifies test methods to verify the electrostatic properties of the garments, such as surface resistivity and puncture resistance
Applications : EN 1149-5 is relevant for many sectors, including petrochemical industry, food processing, metallurgy, chemical industry, and others where explosive atmospheres may be present
ELECTRICAL ARC PROTECTIVE CLOTHING

EN ISO 11612:2015
The IEC 61482-2:2018 standard, associated with a 4 kA arc flash test (APC 1), indicates that the garment provides protection against a 4 kiloampere electric arc
The ATPV of 9.7 cal/cm² means the garment offers protection with a 50% probability of second-degree burns when exposed to an arc energy of 9.7 cal/cm², according to Mascot The ELIM of 9.0 cal/cm² represents the maximum energy level the garment can withstand without risk of injury, according to Mascot
IEC 61482-2 : International standard for protective clothing against the thermal hazards of electric arcs
APC 1 : Arc protection class, tested with a 4 kA arc
ATPV (Arc Thermal Performance Value) : Arc energy that the garment can withstand with a 50% risk of second-degree burns
ELIM (Incident Energy Limit) : Maximum arc energy level that the garment can withstand without risk of injury
WELDING PROTECTIVE CLOTHING
EN ISO 11611:2015
The standard EN ISO 11611:2015, class 1, levels A1 and A2, concerns protective clothing for welders and related trades. It specifies the minimum safety requirements and test methods for protective clothing, including hoods, aprons, sleeves, and gaiters, designed to protect the wearer’s body, head, and feet during welding operations and similar techniques
Requirements of the EN ISO 11611:2015 standard :
Class 1 : Provides protection against welding techniques and less hazardous situations with low levels of spatter and radiant heat
A1 (limited flame spread) : Indicates that the garment meets the requirements for limited flame spread in case of surface ignition
A2 (limited flame spread) : Indicates that the garment meets the requirements for limited flame spread in case of edge ignition
HIGH VISIBILITY CLOTHING

EN 17353
The EN 17353 standard is titled "Enhanced Visibility Equipment for Moderate Risk Situations." It concerns clothing and devices designed to improve the visibility of the user in situations where risks are considered moderate. This standard is gradually replacing the older EN 1150 and EN 13356 standards for non-professional clothing and is complementary to the EN 20471 standard for high visibility
Three types of classifications :
Type A : Garments for daytime use only
Type B : Garments for use in darkness, with retroreflective materials
Type AB : Garments combining the requirements of Types A and B, providing visibility in all lighting conditions
Key points of the EN 17353 standard :
Fluorescent materials : Garments must have a minimum surface area of fluorescent material (0.24 m²)
Distribution of fluorescent material : The fluorescent material must be distributed across the entire garment for 360° visibility
Retroreflective strips : They must be present to ensure visibility in darkness, with a minimum width of 20 mm
Versatile use : The standard can be applied to workwear as well as multi-risk protective clothing (ATEX zones)
WEATHERPROOF PROTECTIVE CLOTHING

EN 343
The EN 343 standard concerns protection against weather conditions, specifically rain and fog. It specifies the requirements for workwear designed to protect against rain, snow, fog, and ground moisture
Key points of the EN 343 standard :
Waterproofness (resistance to water penetration) : The garment is rated from 1 to 3, with 3 being the most waterproof
Breathability (evaporative resistance) : The garment is also rated from 1 to 3, with 3 being the most breathable
Seam strength : The seams of EN 343 certified garments are tested for their resistance to rain
Shrinkage : The materials used to make the garments are tested for shrinkage after washing (limited to 3% for woven materials and 5% for knitted materials)
What are the standards for
Disposable Masks (respiratory protection) ?FFP1
Maximum using time : 8h00
Nominal Protection Factor** X4Particles without specific toxicity and water-based aerosols
Ex : Cotton, graphite, sodium hydroxide, calcium carbonate, cement, cellulose...
CE - EN149FFP2
Maximum using time : 8h00
Nominal Protection Factor** X12
Solid and / or liquid aerosols indicated as dangerous or irritant
Ex : softwoods, metals, resin, fiberglass, mineral fiber, charcoal...
CE - EN149FFP3
Maximum using time : 8h00
Nominal Protection Factor** X50
Toxic solid and / or liquid aerosols
Ex : hardwoods, ceramic, rock wool, cadmium, chromium, powdered pesticide...
CE - EN149EN ISO 149 : Specification of respiratory protection devices (filtering half-masks):
This standard specifies the minimum characteristics to be required of filtering half-masks used as respiratory protection devices against particles. It defines three classes of filtration efficiency, namely FFP1, FFP2 and FFP3 * TIL : Leaking of the ambiant atmosphere into the respiratory interface mesured in laboratory
* TIL : Leaking of the ambiant atmosphere into the respiratory interface mesured in laboratory
** FPN : Nominal Protection Factor corresponds to the level of protection tested in the laboratory. The nivel of APF, Assigned Protection Factor, might be different according local regulationsWhat are the standards for
Protective Clothing (body protection) ?HIGH VISIBILITY CLOTHING
EN ISO 20471 :This standard specifies the requirements for protective clothing aiming to signal the presence of the wearer visually, so that he may be detected and seen in hazardous situations, in all conditions of daylight, and night under illumination of car headlights. There are three classes of high-visibility colthing. Each class must have minimum surfaces of visible material constituing the garnment. The higher the class, the more visible the garnment.

Marking :
X : Class of high visiblity surface (From 1 to 3)PROTECTIVE CLOTHING AGAINST RAIN
EN ISO 343 :This standard specifies the requirements and test methods applicable to the materials and seams of protective clothing against foul weather (for example precipitation in the form of rain or snow), fog and ground humidity
 X : Résistance to water penetration, Wp
X : Résistance to water penetration, Wp
X : Water vapour resistance, RetWhat are the standards for
Disposable Coverall (chemical protection) ?

EN ISO 13034 :
Protective clothing against liquid chemicals (splashes)
EN ISO 13982-1 :
Protective clothing for use against solid particules (dust-asbestos)
EN ISO 14605 :
Protective clothing for use against liquid chemicals (sprays-fogs)
EN ISO 1149-5 :
Protective clothing to dissipate static electricity
EN ISO 1073-2 :Protective clothing against radioactive contamination
EN ISO 14126 :Protective clothing against infective agents
What are the standards for
Safety helmets (head protection) ?
EN ISO 397 : Safety helmets for the industryMandatory Tests :
Impact * : The force transmitted to the test head must not exceed 5kN when a 5kg object falls from a height of 1m
Penetration* : The point of the test mass (3kg at 1m) must not come into contact with the skull
Flammability : The helmet must not burn for more than 5 seconds after the flame is removed
*Impact and penetration tests must be conducted at -10°C, ambient temperature, and +50°C
Optional Tests :
Extreme Temperatures : Impact and penetration tests are conducted at ambient temperature, +150°C, -20°C, or -30°C
Electrical Contact Protection : Protects against accidental short-term contact with live electrical conductors up to 440VAC
Lateral Compression Protection : The maximum deformation of the helmet must be less than or equal to 40mm
Resistance to molten metal splashEN ISO 50365 : Electrically insulating helmets for use in low voltage environments
Mandatory Tests :
Electrically Insulating Helmets for use on or near live installations not exceeding 1000VAC or 1500VDC (Electrical Class 0)
When used together with other electrically insulating protective equipment, these helmets prevent dangerous currents from passing through the body via the head
These optional electrical insulation tests are more stringent than those of the EN397 standard and complement them (marked with two triangles, Class 0)EN ISO 812 : Head protection bumper caps for the industry
Mandatory Tests :
Impact * : This PPE protects against impacts from collisions with structures or objects. It does not protect against impacts resulting from the fall of an object
The impact energy on the helmet peak at the end of the test reaches 12.25J
Penetration* : The point of the test mass (0.5kg at 0.5m) must not come into contact with the skull
*Impact and penetration tests must be conducted at -10°C, ambient temperature, and +50°C
Optional Tests :
Extreme Temperatures : Impact and penetration tests are conducted at ambient temperature, -20°C, or -30°C
Electrical Contact Protection : Protects against accidental short-term contact with live electrical conductors up to 440VAC
Flammability : The cap must not burn with flame emission for more than 5 seconds after the flame is removed (marked F)
What are the standards for
Safety glasses (eye protection) ?ISO STANDARDS
EN 166 : Applies to all types of individual eye protectors against hazards that may damage the eye, except for radiation from nuclear sources, X-rays, laser emissions, and infrared radiation emitted by low-temperature sources. It does not apply to eye protectors for which separate standards exist (laser eye protection, general-use sunglasses, etc.)
Meaning of Symbols - EN 166 :
Mandatory performances :
1 : Optical Class allowing for the permanent wearing of the glasses
S : Reinforced Strength : A 22mm diameter ball launched at 5.1 m/s (18.36 km/h)
F : Low Energy Impact : A 6mm diameter ball launched at 45 m/s (162 km/h)
B : Medium Energy Impact : A 6mm diameter ball launched at 120 m/s (432 km/h)
A : High Energy Impact : A 6mm diameter ball launched at 190 m/s (684 km/h)Optional performances :
3 : Resistance to liquids (droplets & splashes)
4 : Resistance to large dust particles (size > 5 microns)
5 : Resistance to gases and fine dust particles (size < 5 microns)
8 : Resistance to electric arc from short circuits
9 : Resistance to molten metal splashes and hot solids
T : (F - B - A) Mechanical resistance to extreme temperatures -5°C / +55°C
N : Resistance to fogging of lenses
K : Resistance to surface damage from fine particles (anti-scratch)EN 175 : Specifications for safety requirements for eye and face protection equipment for welding and related techniques (frames/supports for filters)
EN 169 : Specifications for the gradation numbers and requirements for the transmission factor of filters designed to protect operators in welding and related techniques. Specifications for dual gradation number welding filters
EN 170 : Specifications for the gradation numbers and requirements for the transmission factor of filters for protection against ultraviolet radiation
EN 172 : Specifications for the gradation numbers and requirements for the transmission factor of filters for protection against solar radiation, industrial use
EN 379 : Specifications for automatic welding filters, i.e., welding screens with automatic adjustment of the transmission factor. These screens are designed to protect operators in welding and related techniques
EN 1731 : Specifications for the materials, design, performance, and testing methods for mesh-type eye and face protectors, for professional use
OUR PRODUCTS' ADVANTAGES
5 good reasons to use our PPE products

ROBUSTNESS

STANDARDS

PRICE

COMFORT

DESIGN
FRAGMENT SAFETY - PPE Provider for Africa and Tropical Countries
PPE Provider in Africa - Safety Shoes for Africa - Personal Protective Equipment for Africa - Mining Workwear Africa - Petrol Workwear Africa - Safety Boots for Africa - Workwear Supplier in Africa - Rain Protective Clothes - High Visibility Clothes - Personal Protective Equipment Supplier in Africa
All rights reserved - 2026 - Website made by DEL CARIBE